We must also keep an eye out for potential crypto scams trying to ruin the fun. This is because scammers become more active during the holidays, targeting us while we have our guard down.

Ashish Nanda, Deakin University; Jeb Webb, Deakin University; Jongkil Jay Jeong, Deakin University; Mohammad Reza Nosouhi, Deakin University, and Syed Wajid Ali Shah, Deakin University
Each year, as the festive season arrives, we must also keep an eye out for potential scammers trying to ruin the fun. This is because scammers become more active during the holidays, targeting us while we have our guard down.
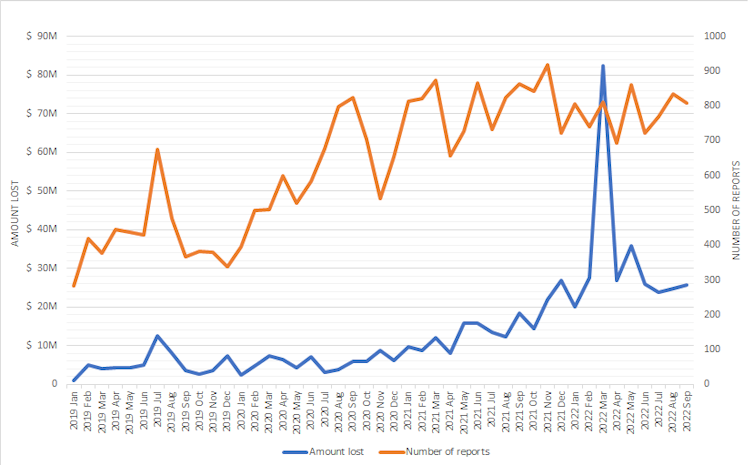
So far in 2022, Australians have lost around half a billion dollars to scams, which is already significantly more than had been lost by this time last year. The majority of these losses – around $300 million – have involved investment or cryptocurrency scams.
scamwatch.gov.au
Researchers from Deakin University’s Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation had a opportunity to interview recent victims of these scams. Here is what we found.
Read Also: Careful lovebirds, scammers targeting you on social media
Anyone can fall for a scam
I was shocked and could not accept that this happened to me although I was very careful […] I was numb for a couple of minutes as it was a large amount of money. – (26-year-old female office manager from South Australia)
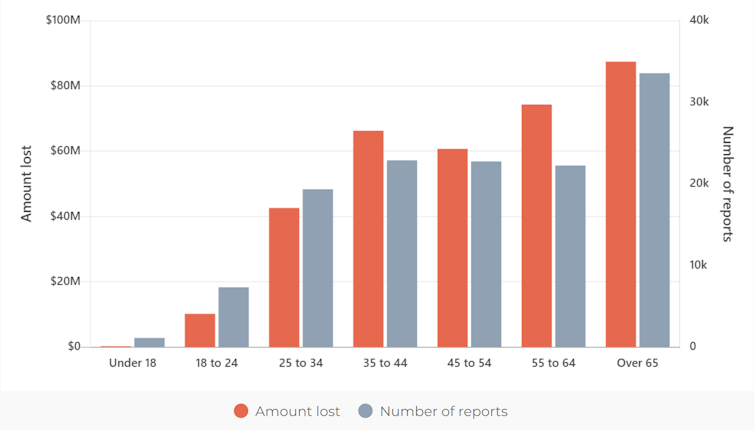
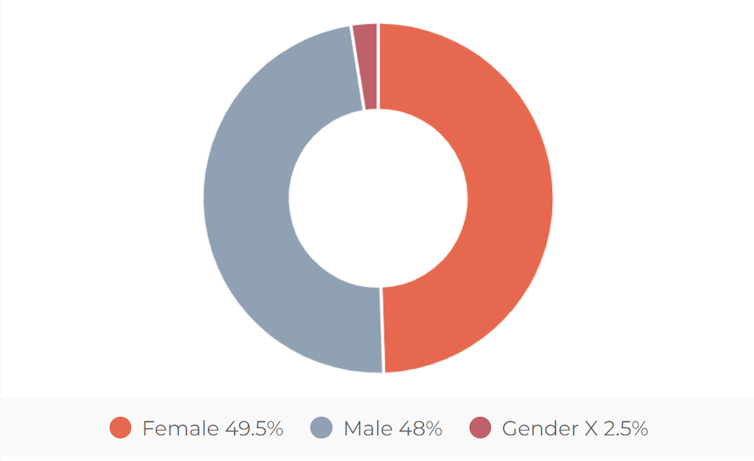
These scams have become highly sophisticated and criminals have become less discriminating about whom they target. This is reflected in recent victim demographics, showing a wide variety of backgrounds, a more even distribution across several age groups, and an almost even split on gender.
scamwatch.gov.au
scamwatch.gov.au
So, how can you spot these scams and where can you get help if you have fallen victim?
If it sounds too good to be true, it might just be a scam
I was dumbfounded, to say that ground shattered under my feet would be an understatement, it will take me a very long time to recover from it, financially and mentally. – (36-year-old female, legal practitioner from Victoria)
Most crypto scams involve getting the victim to buy and send cryptocurrency to the perpetrator’s account for what appears to be a legitimate investment opportunity.
Cryptocurrency is the currency of choice for this type of crime, because it’s unregulated, untraceable and transactions cannot be reversed.
Victims of such scams are targeted using a number of different methods, which include:
Investment scams: scammers pretend to be investment managers claiming high returns on crypto investments. They get the victim to transfer over funds and escape with them.
“Pump and dump”: scammers usually hype up a new cryptocurrency or an NFT project and artificially increase its value. Once enough victims invest, the scammers sell their stake, leaving the victims with worthless cryptocurrency or NFT.
Romance scams: involves scammers using dating platforms, social media or direct messaging to engage with you, gain your trust and pitch an amazing investment opportunity promising high returns, or ask for cryptocurrency to cover medical or travel expenses.
Phishing scams: an old but still effective scam involving malicious emails or messages with links to fake websites promising huge returns on investment or just outright stealing credentials to access users’ digital currency wallets.
Ponzi schemes: a type of investment scam where the scammers use cryptocurrency gathered from multiple victims to repay high interest to some of them; when victims invest more funds, the scammers escape with all the investments.
Mining scams: scammers try and convince victims to buy cryptocurrency to use in mining more of it, while in reality there is no mining happening – the scammers just make transfers that look like returns on the investment. Over time, the victim invests more, and the scammers keep taking it all.
Although methods evolve and change, the telltale signs of a potential scam remain relatively similar:
- very high returns with promises of little or no risk
- proprietary or secretive strategies to gain an advantage
- lack of liquidity, requiring a minimum accumulation amount before funds are released.
Where to seek help if you’ve been scammed
I felt helpless, I didn’t know what to do, who to reach out to, I was too embarrassed and just kept blaming myself. – (72-year-old male, accountant from Victoria)
If you think you have fallen victim to one of these scams, here is what you need to do next:
- inform the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) here or reach out to relevant authorities as per advice on the ScamWatch website
- reach out to your friends and family members and inform them of the scam; they can also be a source of help and support during such times
- as these events can have a psychological impact, it’s recommended you talk to your GP, a health professional, or someone you trust
- you can also reach out to counselling services such as LifeLine, beyond blue, Sucide Call Back Service, Mens Line, and more for help and support.
If you ever find yourself in a difficult situation, please remember help and support is available.
Finally, to prevent yourself becoming the next statistic over the holiday period, keep in mind the following advice:![]()
- don’t share your personal details with people online or over a call
- don’t invest in something you don’t understand
- if in doubt, talk to an expert or search online for resources yourself (don’t believe any links the scammers send you).
Ashish Nanda, CyberCRC Research Fellow, Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation (CSRI), Deakin University; Jeb Webb, Senior Research Fellow, Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation (CSRI), Deakin University; Jongkil Jay Jeong, CyberCRC Senior Research Fellow, Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation (CSRI), Deakin University; Mohammad Reza Nosouhi, CyberCRC Research Fellow, Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation (CSRI), Deakin University, Deakin University, and Syed Wajid Ali Shah, CSCRC Research Fellow, Centre for Cyber Security Research and Innovation, Deakin University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.











